[Machine Learning]Reinforcement Learning
複習
機器學習可以被分為三大類:
-
Supervised Learning:
Learn to generalize and classify new data based on labelled training data. 像是 regression 和 classification 就屬於 Supervised Learning。 -
Unsupervised Learning:
Discover structure and relationships in complex high-dimensional data. 像是 cluster。 -
Reinforcement Learning:
Generate policies/strategies that lead to a (possibly delayed) reward. Learn by interacting with the environment! 和人類學習的過程很像,會根據環境而行動,並做調整(像是學騎腳踏車)。這篇主要就是要介紹 Reinforcement Learning。
Reinforcement Learning 可以做什麼?
- 2016 年 AlphaGo 擊敗世界棋王使用的就是 Reinforcement Learning
- Robot Learns to Flip Pancakes
- pole balancing
Differences to other methods
- Difference to supervised learning
- Time! Reinforcement Learning 的學習時間會比 Supervised Learning 費時(當然要有缺點,不然大家幹嘛還要用 Supervised Learning),所以如果有 labels 通常還是會選用 Supervised Learning,但當事前沒有 labels,不知道結果的時候就可以使用 Reinforcement Learning。
- Can become better than the system designer, unlike a supervised system that can never become better than the teacher. 因為 Supervised Learning 是根據 system designer 給的 labels 下去計算,但 Reinforcement Learning 是機器自己學習所獲得的結果,就像是,雖然教練教學生打球,但學生的學習成果可能比教練還好。
- Feedback is usually not immediate but is given after many actions - delayed feedback! 像是下棋,要等到結果贏或輸才會知道是得到 positive reward 還是 negative reward。
- Feedback is given as a scalar reward, not as the correct action to make. Supervised Learning 的 feedback 是結果是否正確,但 Reinforcement Learning 得到的 feedback 是 reward(can be positive or negative)。
- Difference to control theory
- No physical model of the world, e.g., in pole balancing
機器怎麼學?
不像 Supervised Learning 有 lable 可以知道結果是正確還是錯誤, Reinforcement Learning 的學習方法是透過 reward 來知道學習結果正確或不正確(就像是狗狗學習技能,如果做對了就給東西吃一樣)。所以透過打分數的結果來知道怎麼樣的行為是正確的而進行調整,往正確的學習道路邁進。(所以每次學習結果所獲得的 reward 就變得有點像是 Supervised Learning 的 labels 的感覺,只是這個 labels 是從學習的過程中獲得的)
Reinforcement Learning 如何進行?
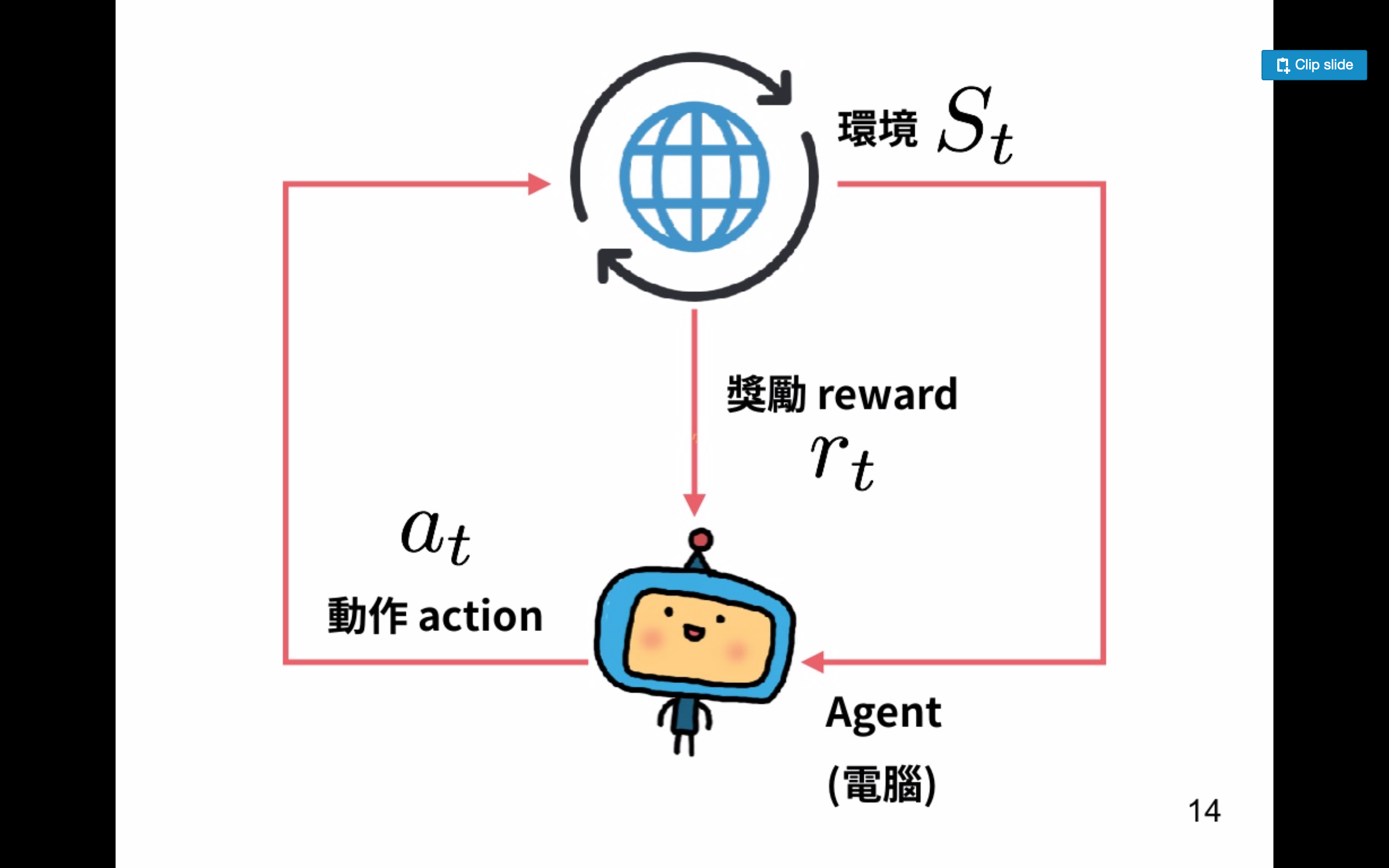
Reinforcement Learning 問題的基本設定
<A, S, R, P>
- Action space : A
- State space : S
- Reward: R : S × A × S → R
- Transition : P :S × A → S
A 代表的是 Agent 的所有動作(action);S 是 state,是 Agent 所能感知的狀態; R 是 reward 代表獎勵或懲罰,是一個實數;P 是 Agent 所交互的世界,也被稱為 model。
根據上圖(Source),電腦是 agent,地球代表 environment(環境),reward(獎勵)是環境所提供的反饋,reward 由模型設計者定義,可以是 positive 或是 negative,reward 的定義對強化學習來說是個很重要的一環。
Policy
Policy 就是 agent 根據每個 state 所做出的不同的 action,也就是根據不同的狀態 agent 會採取不同的「策略」。定義為 \(\pi\),是 RL(Reinforcement Learning) 最核心的問題。可以將 policy 看成是當 agent 感知到 state(S) 採取 action(A) 的 mapping。policy 可以分為隨機的(stochastic policy)和確定性的(deterministic policy)。
- stochastic policy: \(\pi(a\mid s),~ and \sum\pi(a\mid s) = 1\)
- deterministic policy: \(\pi(s)\)
Reward
Reward 是 RL 非常重要的一環,沒有 reward,agent 就不會知道到底學習正確還是錯誤。透過 reward,agent 才知道剛剛採取的 action 好不好。以下圖(Source)為例,最一開始的 state 是 \(s_0\),agent 做了 \(a_0\) 的 action,這時候產生了一個 reward \(r_1\),然後因為剛剛的 \(a_0\) 這時候 state 來到 \(s_1\),而 agent 要採取下一步 \(a_1\) 的時候就會根據剛剛的 \(r_1\) 來反應。agent 就這樣一步一步根據 reward 的結果來學習。
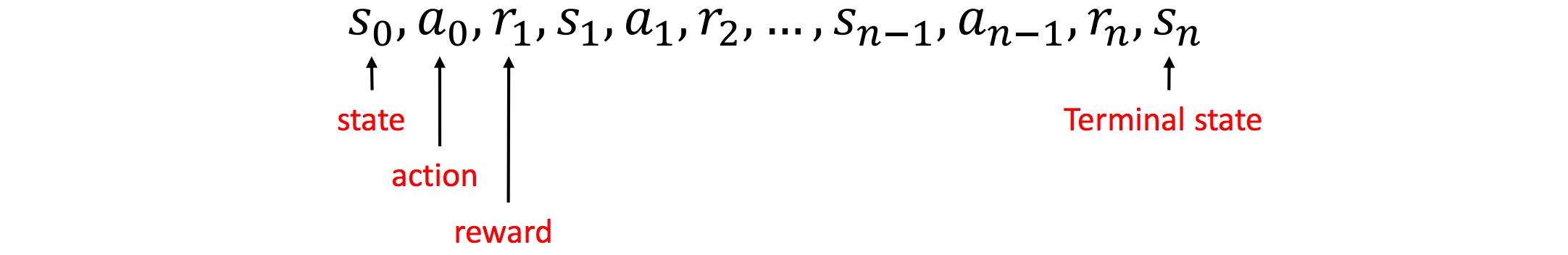
但其實並不是所有的學習都會像這個例子一樣立即獲得 reward,像下棋就會是整局結束後才得到 reward。
另外,需要注意的是,Reward \(\ne\) Goal。也就是說,agent 的目標並不是「當前」reward 最大,而是「平均累計」回報最大。
總結來說,Reinforcement Learning 的目標就是找到一個最佳的 Policy(策略),讓最後平均的 reward 最大!
所以現在問題就來了,要如何衡量這個 policy 好不好?哪些 policies 是我們想要 explore 的?
Value function
Value function - How good is a policy?
定義從長期來看 action 平均回報的好壞。例如,象棋中吃掉對方的車看起來即時收益很大,但如果因為吃掉對方的車自己的將卻被吃了,那麼從長期看這個 action 就不是一個好的選擇。
\(V_\pi(s)\) 表示的是策略 \(\pi\),狀態 s 的長期期望收益。\(Q_\pi(s, a)\) 是策略 \(\pi\) 在狀態 s 下,採取動作 a 的長期期望收益。
-
長期回報期望:\(G_t = \sum_{n=0}^{N}\gamma^nr_{t+n}, ~ where ~ 0 < \gamma < 1\) (因為 \(\gamma\) 介於 0 和 1 之間,所以 makes immediate rewards more important than distant rewards)
-
Value function:\(V_\pi(s) = E_\pi[G_t\mid S_t = s]\)
-
Q function:\(Q_\pi(s, a) = E_\pi[G_t\mid S_t = s, A_t = a]\)
How to learn V(s)?
-
Monte Carlo approach
-
Temporal Difference approach
Summary
- For a given policy, the value (expected reward) V(s) of each state is unknown before we learn it by interacting with the environment.
- V(s) is found iteratively, starting for example with V(s)←0, using the Monte Carlo or Temporal Difference methods.
- The Temporal Difference method generally converges much faster.
Q-Learning
Which policies should we explore?
上面介紹了 V(s) 是狀態 s 的長期期望收益,那 agent 要如何決定根據它來決定要做什麼 action 採取什麼 policies 呢?這時候我們就會加上 action 這個變數來看,也就是上面提到的 Q(s, a)。
- \(V^*(s) = \max_{a} Q(s_{k+1}, a)\) denote the value function for the optimal policy
- \(Q(s, a)\) is expected future reward of doing action a in state s and then following the optimal policy \(Q(s_k, a) = r(s_k, a) + \gamma V^*(s_{k+1})\)
- \(Q(s, a)\) 未知,必須透過學習得到。
\(Q(s_k, a_j) \leftarrow (1 - \eta) Q(s_k, a_j) + \eta (r + \gamma \max_{a} Q(s_{k+1}, a))\), \(\eta\) is learning rate
這篇文章翻譯了這個原文,我覺得非常好理解。但要整篇整理在這裡太麻煩了,所以自己看吧。
Reference:
Linköping University Neural Networks and Learning Systems TBMI26 / 732A55 2019 Lectures.
深度强化学习(Deep Reinforcement Learning)入门:RL base & DQN-DDPG-A3C introduction
wikipedia - 強化學習
強化學習 Reinforcement Learning
莫凡python
[機器學習 ML NOTE] Reinforcement Learning 強化學習(DQN原理)
如何用简单例子讲解 Q - learning 的具体过程?
A Painless Q-learning Tutorial (一个 Q-learning 算法的简明教程)
