[Machine Learning]Decision Tree
Decision Tree
Decision Tree是什麼?
簡單來說,decision tree 是一個分類模型。
- Tree-based methods partition the feature space into a set of rectangles, and then fit a simple model (like a constant) in each one.
這是 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning 裡頭的定義。
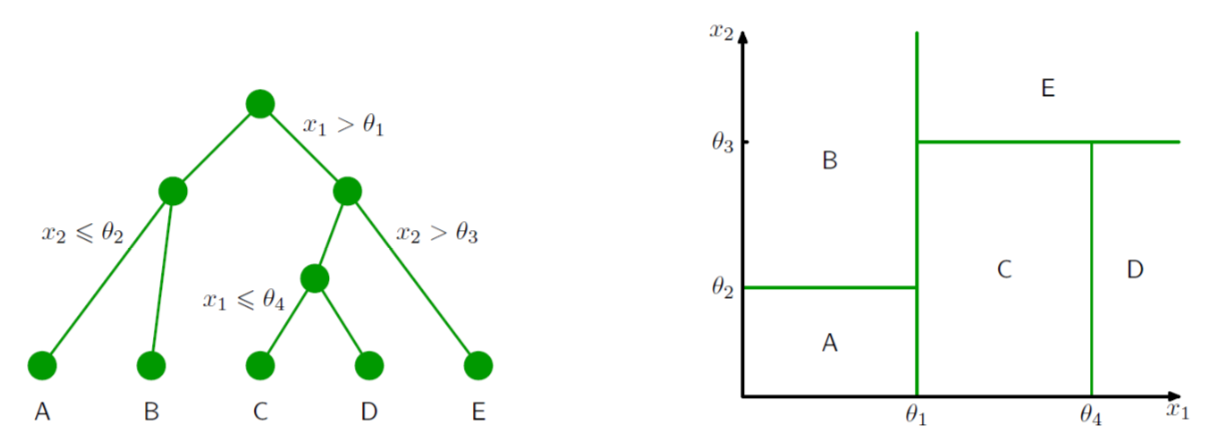
根據上圖,想像一下,在右邊的二維座標平面上有一堆散布的點,而 decision tree,就是將這個平面一一分割,每一個框框都是一個分類結果。但我們可以用右邊那樣一層一層的樹枝結構狀來表示右邊難懂的圖。(這裡的例子是二維平面,當變數 \(x_i\) 增加時,這樣的概念可以推廣到多維空間)
每一個分支都像是一個 if-else 問題,如果是就選某一邊,不是就選另外一邊。
上圖左,我們可以看到有兩個變數,\(x_1\), \(x_2\),第一關是 \(x_1 > \theta_1 \),如果小於就往左邊分,如果大於就往右邊分,以此類推往下繼續細分,最後給予分類結果。最後共分成 A, B, C, D, E 五個類別,也就是右邊的五個框框。
Decision Tree 又可以分為
-
Regression trees - 最後分類結果為連續變數
-
Classification trees - 最後分類結果為類別變數
名詞
- Root node (The Root) - 第一個起始的點
- (Internal) Nodes - 中間的節點。上方會有箭頭指向 node,且 node 也會往下指向其他點。
- Leaves (terminal nodes) - 最後的節點,也就是最後的分類結果。
如何分類?
假如今天我有一份 data,decision tree 是如何決定要先使用哪一個變數與什麼值作為分割呢?
分割的原則是,這樣的分割要能得到最大的資訊增益 (Information gain, IG) ([資料分析&機器學習] 第3.5講 : 決策樹(Decision Tree)以及隨機森林)
資訊量根據最後的分類結果可以使用,
- Regression trees:
- MSE (mean-squared error)
- Classification trees:
- Entropy (Deviance)
- Gini impurity
- Missclassification error
在 Classification tree 裡,Entropy 和 Gini impurity 是常用的兩種方式, 詳細的公式請參考 Wikipedia
假如今天碰到兩種 model 算出來的資訊量都ㄧ樣,請選擇比較簡單的那個 model。(分支、leaves node 較少)
R 範例 這裡使用 tree 這個 library 做範例,另外還有像是 rpart 也是做 decision 常用的 package。
library(tree)
data("iris")
# 使用 Entropy (Deviance)
fit <- tree(Species ~ Sepal.Length + Petal.Length, iris, split = c("deviance"))
plot(fit)
text(fit, pretty=0)
summary(fit)
# 使用 Gini impurity
fit <- tree(Species ~ Sepal.Length + Petal.Length, iris, split = c("gini"))
plot(fit)
text(fit, pretty=0)
summary(fit)
優缺點
- 優點:
- Simple to understand and interpret. 容易理解與解釋
- Able to handle both numerical and categorical data. 可以用在類別與 numerical 資料
- 缺點
- Low bias and high variance with respect to the training data. (當 decision tree model 變得太過複雜時,太多 nodes,就會導致 overfitting (bias-variance trade off 的狀況)
所以為了讓 model 不要 overfitting,我們可以使用 pruning 的方式,砍掉底下的樹枝。
在 R 可以使用,prune.tree(),並且可以使用 best 這個參數來決定最後要保留多少 leaves。
使用剛剛最後的 fit示範
prune_fit <- prune.tree(fit, best = 5)
plot(prune_fit)
text(prune_fit, pretty=0)
summary(prune_fit)
這時候 leaves 由原本的 9,修剪到了剩下 5,但 Misclassification error rate 卻是相同的。修剪過後的 model 較簡單,且 variance 也會比較小,在預測上表現也會較佳。
Reference:
[資料分析&機器學習] 第3.5講 : 決策樹(Decision Tree)以及隨機森林
StatQuest: Decision Trees
The Elements of Statistical Learning
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
