[統計]離散型(Discrete)隨機變數與其機率分佈(3)
這一系列我是以
Wackerley, Mendenhall and Scheaffer 的
Mathematical Statistics with Applications, 7th edition 這本書為主,
有些名詞與定理解釋會再參考其他書籍與網路作為輔助(下方有參考連結)。
這一篇要介紹常見的離散型分佈(Discrete Distribution),這篇主要是參考 Source
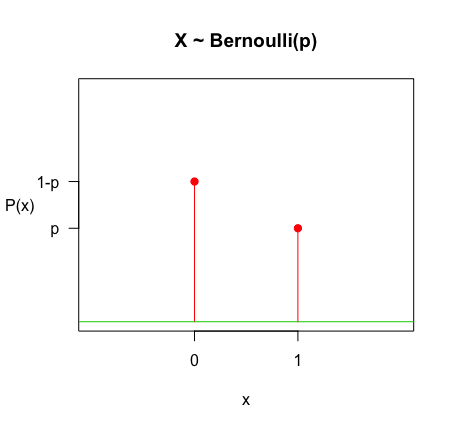
伯努利分佈 Bernoulli Distribution
定義 Definition
- A random variable \(X\) is said to be a bernoulli random variable with peremeter \(p\), shown as \(X \sim Bernoulli(p)\), if its PMF is given by
- where \(0 < p < 1\)
簡單來說,一個事件只有兩種可能。
生活中有非常多的例子都會是 Bernoulli Distribution,譬如,
- 考試有及格、不及格
- 丟擲一枚銅板有正面、反面
- 小孩子性別可能是男生、女生
幾何分布 Geometric Distribution
定義 Definition
- A random variable \(X\) is said to be a geometric random variable with peremeter \(p\), shown as \(X \sim Geometric(p)\), if its PMF is given by
- where \(0 < p < 1\)
Geometric Distribution 的例子:擲一枚銅板,且此銅板擲到 Head 的機率為 \(p\)。今天擲這枚到出現第一個 Head 為止,則其機率分佈為 Geometric Distribution。
另外,每一次擲這枚銅板都會是獨立的 Bernoulli 試驗。
所以,Geometric Distribution 就是很多次的 Bernoulli 試驗直到成功為止。
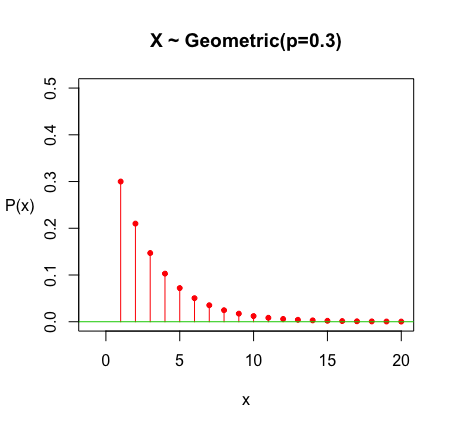
以 \(p = 0.3\) 為例,其 Geometric Distribution 的 PMF 會是這樣,
二項分布 Binomial Distribution
定義 Definition
- A random variable \(X\) is said to be a binomial random variable with peremeter \(n\) and \(p\), shown as \(X \sim Binomial(n, p)\), if its PMF is given by
- where \(0 < p < 1\)
Binomial Distribution 也是很多次獨立 Bernoulli 試驗的結果,但和 Geometric Distribution 不一樣的是,Binomial Distribution 會執行 \(n\) 次的 Bernoulli 試驗,且成功了 \(k\) 次。
所以它的 PMF 會有 \(\left( \begin{array}{c} n \\ k \end{array} \right)\),表示執行了\(n\) 次,其中有 \(k\) 次成功,且這 \(k\) 次並沒有限定在哪個位置。
可以以丟擲 \(n\) 枚銅板來想,其中 \(k\) 枚硬幣為 Head,\((n-k)\) 為 Tail。
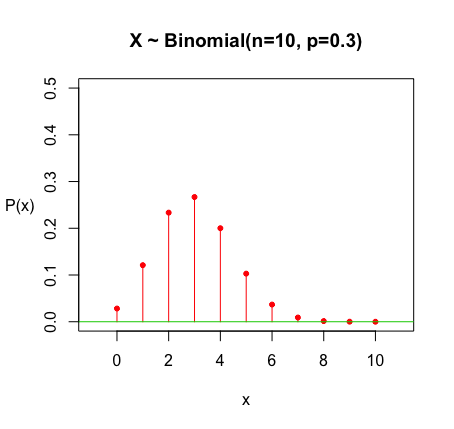
以 \(n = 10,\; p = 0.3\) 為例,其 PMF 圖會是,
Binomial random variable as a sum of Bernoulli random variables
- If \(X_1,\;X_2,\;X_3,…,\;X_n\) are independent \(Bernoulli(p)\) random variable, then the random variable \(X\) defined by \(X = X_1 + X_2 + X_3 + … + X_n\) has a \(Binomial(n,p)\) distribution.
也就是,二項分布可以看成是每個獨立的伯努利分佈的和。
布瓦松分布 Poisson Distribution
定義 Definition
- A random variable \(X\) is said to be a poisson random variable with peremeter \(\lambda\), shown as \(X \sim Poisson(\lambda)\), if its range is \(R_X = \{ 0, 1, 2, 3,… \} \), and if its PMF is given by
Poisson Distribution 的意義為:單位時間內,事件出現平均 \(lambda\) 次的機率分布。
既然上面的式子為 PMF,那我們來檢驗 \(\sum_{k \in R_X}{P_k(x)} = 1\) 是否正確。
\[\begin{align} \sum_{k \in R_X}{P_k(x)} &= \sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \frac{e^{-\lambda} \lambda^k}{k!} \\ &= e^{-\lambda} \sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \frac{\lambda^k}{k!} \\ \end{align}\]\[\begin{align} &= e^{-\lambda} e^{\lambda} \\ &= 1 \\ \end{align}\]Note: 根據 Taylor Series(泰勒展開式) \(\; e^{x} = \sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \frac{x^k}{k!}\),上列式子可以寫成,
Example:
The number of emails that I get in a weekday can be modeled by a Poisson distribution with an average of 0.2 emails per minute.
- What is the probability that I get no emails in an interval of length 5 minutes?
- What is the probability that I get more than 3 emails in an interval of length 10 minutes?
Poisson as an approximation for binomial
- Let \(X \sim Binomial(n, p = \frac{\lambda}{n})\), where \(\lambda > 0\) is fixed. Then for any \(k \in {0, 1, 2,…} \), we have
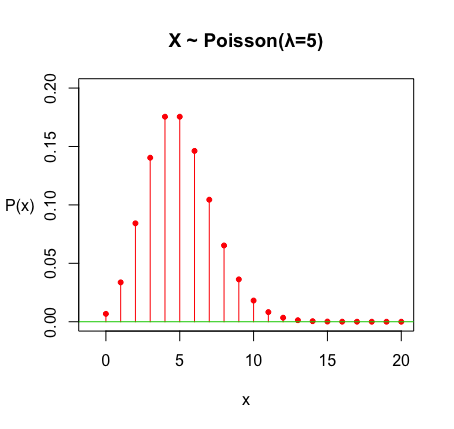
\(X \sim Poisson(\lambda = 5)\) 的函數圖形,
參考:
